Location: Central Europe
Global Gender Gap in Unpaid Care: Why Domestic Work Still Remains a Woman’s Burden

In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous reports point to the fact that women are mainly shouldering the burden of increased domestic care duties. But even before the pandemic struck, women performed more than two-thirds of the unpaid domestic care work in both developing and developed countries. The lack of gender parity in the distribution of domestic work is associated with significant economic inefficiencies, as well as considerable social and economic consequences for women – affecting their bargaining power within the household and their labor market outcomes in particular. In the brief, the author reviews the literature on both the economic and sociological factors which perpetuate the pattern of gender disparity in unpaid domestic care work. The author also summarizes the “recognize, reduce and redistribute” policies which could be adopted to help address the problem.
Country Reports
| Armenia country report (EN) | Armenian language version (AM) |
| Belarus country report (EN) | Belarussian language version (BY) |
| Georgia country report (EN) | Georgian language version (GE) |
| Latvia country report (EN) | Latvian language version (LV) |
| Poland country report (EN) | Polish language version (PL) |
| Russia country report (EN) | Russian language version (RU) |
| Ukraine country report (EN) | Ukrainian language version (UA) |
Gender Gap in Unpaid Care: Why Domestic Work Still Remains a Woman’s Burden?
The realities of unpaid care and domestic work have received much attention lately in policy and academic circles, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic (Van Houtven et al., 2020; Craig and Churchill, 2020; Duragova, 2020). Recent surveys and reports confirm that while the unpaid household work burden increased for both genders, women around the world ended up shouldering the lions’ share of various household chores and care duties during the pandemic (UN Women, 2020). For many countries, prolonged lockdowns have put a sudden spotlight on the “hidden” side of people’s economic lives, not typically reflected in the national accounts data. Unsurprisingly, among the main issues connected with unpaid care work is the highly gendered division of labor in the “household sector” and its consequences for the emotional and economic well-being of families. In this policy brief, the author explores the current state and the evolution of gender inequalities in unpaid domestic care work worldwide, and discusses the academic literature which addresses the reasons and the consequences behind them. The author also discusses potential policy interventions which could promote greater work-life balance and help advance both social and family-level welfare.
Gender Gaps in Unpaid Care Work
The term unpaid care and domestic work appears under many terminological guises, including “unpaid care work” “unpaid household work”, “unpaid domestic care work” and others. These terms essentially refer to the same phenomenon – unpaid care activities carried out in the household. They include cooking, cleaning, washing, water and fuel collection, shopping, maintenance, household management, taking care of children and the elderly, and others (Addati et al., 2018). For the purposes of this brief I will use the terms interchangeably, relying mainly on “unpaid care”, “domestic work”, or “unpaid domestic care” to describe these activities. While the value of unpaid care work is not included in the national income accounts, it can be tracked by time-use surveys carried out by national statistical offices in many countries. According to the most recent surveys, (Charmes, 2019) more than three quarters (76.4%) of unpaid domestic care work worldwide is done by women, while 23.6% is done by men. In developed countries, the women’s share is somewhat lower (65%), while in developing and emerging economies, women perform 80.2% of unpaid care. Thus, according to the data, even in developed countries women perform around two thirds of the unpaid domestic care work. Currently, no country in the world seems to have achieved gender parity with regard to the unpaid care distribution in households (U.N. Women., 2019).
Is There Evidence of Convergence in Domestic Care Responsibilities?
Given that the first time use surveys in many countries have been conducted only relatively recently, it may be premature to make claims about changes in the distribution of domestic work and a potential closing of the gender gap. However, evidence from countries with a longer history of time use data, in particular the United States, suggests that the way mothers and fathers allocate their time between paid and unpaid work has changed dramatically between 1965 and 2011. In particular, as can be seen from the Figure 1 (from Parker and Wang, 2013), in 2011 women spent 2.6 times (13 more hours per week) more on paid work, while men spend 5 hours less than in 1965. The time spent on childcare increased for both men and women. At the same time, domestic work hours decreased significantly for women, while somewhat increasing for men.
Figure 1. Moms and Dads, the US 1965-2011: Roles Converge, but Gaps Remain
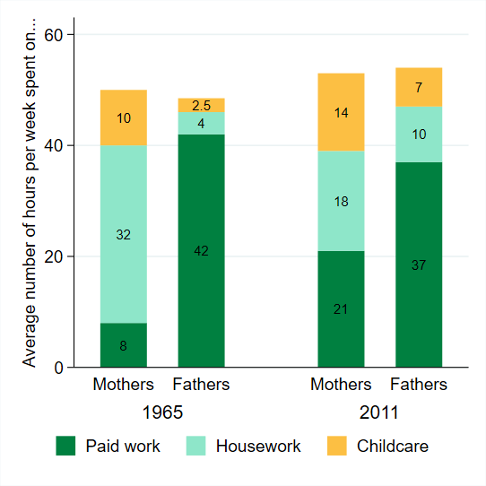
Note: Based on adults aged 18-64 with own child(ren) under the age of 18 living in the household. Source: Parker and Wang (2013).
Overall, analysis of time use survey data over a 40-year span shows a degree of convergence in unpaid care work between men and women (Kan et al., 2011; Altintas and Sullivan, 2016). However, as the Kan et al. (2011) study shows, gender inequality is quite persistent over time. In particular, men concentrate their contribution in domestic work to non-routine tasks (i.e. tasks that generally require less time, have definable boundaries and allow greater discretion around the timing of performance than the more routine tasks) such as shopping and domestic travel, while women devote a bulk of their time to routine work (cooking, cleaning, care). Women’s reduction in domestic work time (especially in routine tasks) may be largely due to the advancement of household technologies and higher acceptance/demand for women’s participation in the labor market (Gershuny, 1983, 2004). Thus, it appears that the “low-hanging fruit” of gender equality within households has already been picked, and, going forward, further shifting of domestic care responsibilities will be a more difficult task, even in developed countries.
Factors That Perpetuate Unpaid Domestic Care as Primarily Women’s Responsibility
The factors responsible for perpetuating gender roles in domestic work can be grouped into economic (specialization, comparative advantage) and sociological (habits, traditions, social perceptions) aspects.
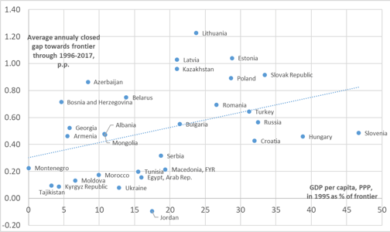
The economic arguments that have long been used to explain the unequal division of paid and unpaid care work rely on the theory of comparative advantage and gains from specialization. Starting from the seminal work of Becker (Becker, 1985), economic models of the family suggested that a division of labor within the household is driven by different experiences and choices to invest in human capital. Becker argued that efficient households require specialization and the pattern of specialization can be explained at least in part by the differences in the initial investment in human capital (market skills for men and household skills for women) (Becker, 2009). In this model, men’s advantage in paid market activities is explained by historical reasons stemming in part from the more physical nature of market work. And yet, contemporary authors point out that the nature of work has been changing over time, with less emphasis put on physical, and more on cognitive skills. Likewise, the nature of household production has been changing (Greenwood et al., 2017). Birth control gave families a better way to control the number of children (Juhn and McCue, 2017). These changes should make men and women’s productivity more equal, and consequently reduce the gender gap between men and women in both types of work. And yet, despite the fact that in developed countries women often achieve higher educational attainment then men (Goldin, Katz and Kuziemko 2006; Murphy and Topel, 2014), it has not been enough to eliminate the gender gap in wages and in the division of unpaid domestic work. Moreover, as the study based on 1992 Canadian data by McFarlane et al. (2000) points out, while the wife’s time in housework increases when the husband spends more time in paid work, the opposite is not necessarily true for men (men do not spend significantly more time on household tasks when their wives increase their employment). Alonso et al., 2019, using a sample of 18 advanced and emerging market economies, find that various factors which determine the allocation of time between paid and unpaid work affect men and women asymmetrically. For example, being employed part time vs. full time considerably increases the participation in unpaid work for women, while for men the same increase is statistically insignificant.
Thus, a purely “pragmatic” economic argument for the household division of labor is not sufficient to explain the persistence of the unpaid care gender gap. Other sociological factors, such as gender roles determined by social attitudes and cultural norms, tend to play an important role in household labor division (Coltrane, 2000; Juhn and McCue, 2017). Moreover, one can argue that educational choices of women, which contribute to their “comparative advantage” in household production, are themselves not independent of cultural norms and attitudes. These choices tend to be shaped in early childhood and reflect how much a family would invest in/encourage a girl’s education vs. that of a boy; whether boys are engaged in certain household chores – cooking, cleaning, caring for young children, etc. (UNDP, 2020). For example, the high gender gap in unpaid domestic work in the South Caucasus can be traced to family patterns. According to survey data (CRRC, 2015) in Azerbaijan, around 96% percent of women were taught in childhood how to cook, clean the house or do laundry, while only 35% of men were taught how to cook and clean. In Georgia, close to 90% of women reported being taught how to cook, clean and do laundry, while less than 30% of men on average reported being taught these skills (UNFPA, 2014).
The Social Cost of Gender Inequality in the Unpaid Care Work Allocation
Gender inequality is not just an issue of fairness. Inequality results in considerable resource misallocation, where women’s productive potential is not fully realized. The study by Alonso et al., 2019 estimates the GDP gains associated with a potential reduction in gender inequality in domestic work to the level observed currently in Norway. Countries like Pakistan and Japan, where the initial gender gap is quite sizeable, would gain around 3 to 4 percent of GDP. Another source of inefficiency is occupational downgrading, a situation where women take jobs below their level of qualification (Connolly and Gregory, 2007; Garnero et al., 2013) in order to better balance their home and work responsibilities. The perception of women as being primarily responsible for childcare and domestic labor drives statistical discrimination in the workplace and affects the “unexplained” portion of the gender pay gap (Blau and Kahn, 2017). The pay gap, in turn, perpetuates inequality in the division of domestic labor. Moreover, perception of unequal domestic work allocation is found to be associated with lower relationship satisfaction, depression, and divorce (Ruppaner et al, 2017). In addition, earlier sociological studies found that inequity in the distribution, rather than the amount of work, causes greater psychological distress (Bird, 1999).
Policies to Address the Gender Gap
Given the sizeable economic and social costs associated with the gender gap in unpaid care work, policy makers are paying greater attention to gender equality and ways to promote work-life balance for men and women. Currently, most solutions center around “recognize, reduce and redistribute” types of policies (Elson, 2017).
The “recognize” policies acknowledge the value of unpaid care work done by women through cash payments linked to raising young children (i.e. maternity leave policies). Most countries in the world adopt publicly funded paid maternity leave policies, although the adequacy of maternity leave payments and the duration of such leaves is still a stumbling block for many countries (Addati et al., 2014). Data suggests that maternity leave of no longer than 12 months has a positive effect on maternal employment, while long leaves (over two years) increase career costs for women (Kunze, 2016; Ruhm, 1998; Kleven et al., 2019)
The “reduce” policies, aim at the provision of public services that would reduce the burden of childcare and other forms of unpaid work on women and free up their time for participation in the labor force. Among such policies are investments in publicly funded childcare services (quality pre-schools and kindergartens) and physical infrastructure to support the provision of clean water, sanitation, energy, and public transport. Empirical studies generally find a positive effect of affordable childcare on female employment rates (Vuri, 2016; Lefebvre et al., 2009; Geyer et al., 2014), but with some caveats – in particular, the subsidies may be less effective for female labor supply if affordable childcare just crowds out other forms of non-parental care (such as informal help from family members) (Vuri, 2016; Havnes and Mogstad, 2011).
Finally, the “redistribute” policies aim to promote the redistribution of household chores and childcare among men and women. Among such policies are initiatives aimed at making flexible and reduced-hour work arrangement attractive and equally available for men and women. (e.g. shifting standard weekly hours to a more family friendly 35 hours per week, as for example in France); active labor market programs aimed at retaining women in the labor market can also help reduce hours devoted to unpaid work (Alonso et al. 2019). Moreover, better labor market regulations (e.g. legislation to regulate vacation time, maximum work hours, etc.) would discourage the long working hours and the breadwinner-caretaker gendered specialization patterns within families (Hook, 2006). Other examples include work-life balance policies recently adopted by the EU (EU Directive 2019/1158), and are aimed at providing paid paternity leave and reserving non-transferrable portions of family childcare leave for men. These policies were found to be effective for both increasing father’s participation in unpaid care and for reducing the gender wage gap within families in a number of country studies (Fernández-Cornejo et al., 2018; Andersen, 2018).
It is important to recognize that more research is needed to identify exactly how and why specific policies may benefit families, and to adapt them to the specific country context. While many of the policies outlined above will not solve the problem of the gender gap overnight, they can be an important first step towards greater global gender equality in the workplace and inside the household.
About FROGEE Policy Briefs
FROGEE Policy Briefs is a special series aimed at providing overviews and the popularization of economic research related to gender equality issues. Debates around policies related to gender equality are often highly politicized. We believe that using arguments derived from the most up to date research-based knowledge would help us build a more fruitful discussion of policy proposals and in the end achieve better outcomes.
The aim of the briefs is to improve the understanding of research-based arguments and their implications, by covering the key theories and the most important findings in areas of special interest to the current debate. The briefs start with short general overviews of a given theme, which are followed by a presentation of country-specific contexts, specific policy challenges, implemented reforms and a discussion of other policy options.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in policy briefs and other publications are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect those of the FREE Network and its research institutes.
Strategies to Opening up After the Pandemic
The Stockholm Institute of Transition Economics (SITE) in collaboration with the FREE Network is delighted to invite you to a webinar to share insights and knowledge on different strategies implemented in vaccination, opening up the borders and the socioeconomic aspects within Sweden, Eastern Europe and the Baltic Sea region, and the Caucasus region.
Since vaccination has started across all over the world, it is vital to reflect upon the road map different countries have chosen to open up societies and economies. How will countries in Eastern Europe and the Baltic Sea region, and the Caucasus region handle the opening of their respective borders and what lies next in line to go back to a pre-pandemic societal routine?
Register
- RSVP: Monday, June 21, 2021, 23:59 (CET, Sweden).
- Location: Online. A link to the webinar will be sent to you 4-5 hours ahead of the start of the webinar.
- Registration: Please register via the Eventbrite platform (see here).
Agenda
The webinar is part of a series of online discussions aiming to provide regional overview updates as well as in-depth analysis of specific topics related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Since the FREE Network includes research and policy institutes in Belarus (BEROC), Latvia (BICEPS), Russia (CEFIR at NES), Poland (CenEA), Georgia (ISET PI), Ukraine (KSE) and Sweden (SITE) the upcoming webinar will provide a comprehensive regional perspective on different strategies implemented in vaccination, opening up the borders and the socio-economic aspect. Learn more about the different strategies in FREE Network countries and ask questions directly to distinguished panelists and experts.
Speakers
- Jesper Roine, Professor at the Stockholm Institute of Transition Economics (SITE/ Sweden)
- Iurii Ganychenko, Senior researcher at Kyiv School of Economics (KSE/Ukraine)
- Lev Lvovskiy, Senior Research Fellow at the Belarusian Economic Research and Outreach Center (BEROC/ Belarus)
- Michal Myck, Director of the Centre for Economic Analysis (CenEA/ Poland)
- Natalya Volchkova, Director of the Centre for Economic and Financial Research at New Economic School (CEFIR at NES/ Russia)
- Sergejs Gubins, Research Fellow at the Baltic International Centre for Economic Policy Studies (BICEPS/ Latvia)
- Giorgi Papava, Lead Economist at ISET Policy Institute (ISET PI/ Georgia)
Chair/Moderator
-
- Anders Olofsgård, Deputy Director of the Stockholm Institute of Transition Economics (SITE) and Associate Professor at the Stockholm School of Economics (SSE)
Jurisdictional Competition for FDI in Developing and Developed Countries

This brief is based on research studying jurisdictional competition between countries and its influence on the inflow of foreign direct investments (FDI). The study compares jurisdictional competition among the developing Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries with competition among developed EU countries. As instruments of jurisdictional competition for FDI, we consider governments’ efforts to improve the rule of law, corporate governance, and tax policies. The results suggest the presence of proactive jurisdictional competition via the quality of corporate governance regulation both in the CEE and the EU countries. The CEE states also attract FDI by competing in tax policies.
Introduction
The determinants of FDI inflows have been examined in numerous studies. A substantial number of them consider the influence of institutions, which are defined as particular organizational entities, procedural devices, and regulatory frameworks (IMF, 2003).
The quality of institutions is a particularly important FDI determinant for less-developed countries because the poor institutional quality and weak law enforcement increase the costs of running a business, create barriers for financial market efficiency, and increase the probability of foreign assets expropriation (Blonigen, 2005).
However, governments interested in attracting FDI to boost job creation, new technologies, and tax revenues to their countries are not only concerned about the internal institutional environment. They are also competing with other countries in attracting foreign investments, engaging in what is often referred to as “jurisdictional competition”. In a broad sense, this can be thought of as governments’ efforts to outcompete one another in offering foreign companies more favorable institutional and fiscal conditions for capital placements.
This brief summarizes the results of a study on the jurisdictional competition for FDI among the developing CEE and among developed EU countries (Mazol and Mazol, 2021). The research explores the precondition for proactive jurisdictional competition between economies for FDI – namely, how the economic and institutional environment within a country impacts the inflow of FDI both domestically and to its neighboring states, – by using a spatial econometric approach. The brief emphasizes the difference in the FDI policy responses implemented by developing CEE and developed EU countries.
Data and Methodology
In our econometric analysis, we use the FDI inward stock (i.e., the value of capital and reserves in the economy attributable to a parent enterprise resident in a different economy) as the dependent variable. The explanatory variables indicating jurisdictional competition include quality of corporate governance, rule of law, political stability, and tax policy. We employ balanced panel datasets for 26 developing CEE countries and 15 developed EU countries for the period 2006-2018. The dataset is derived from the World Bank and UNCTAD databases.
The analysis is based on a panel spatial Durbin error model (SDEM) with fixed effects (LeSage, 2014). Parameter estimates in the SDEM contain a range of information on the relationships between spatial units (in our case, countries). A change in a single observation associated with any given explanatory variable will affect the spatial unit itself (a direct effect) and potentially affect all other spatial units indirectly (a spillover effect) (Elhorst, 2014). The spatial spillover effect is viewed here as the impact of the change in the institutional or economic factor in one country on the performance of other economies (LeSage & Pace, 2009).
In our case, the direct effect is the effect on the FDI in country i of the changes in the studied instrument of jurisdictional competition in country i. The spillover effect is the change in FDI in country j following a change in the studied instrument of jurisdictional competition in country i.
Results
The results of our estimation are suggestive of a proactive jurisdictional competition in taxes among the CEE countries and in corporate governance quality both among the CEE and EU countries. Analyses of other factors (i.e., political stability and rule of law) show no significant interrelation between policy measures implemented by neighboring countries in order to attract FDI.
The precondition for the presence of proactive jurisdictional competition in a particular factor is to have statistical significance in both its direct and spillover effects (Elhorst and Freret, 2009). Such findings may indicate that policy measures in one economy trigger a policy response in a neighboring economy, which, in turn, influences the level of FDI in both countries.
Table 1. Estimation results of SDEM models – direct effects
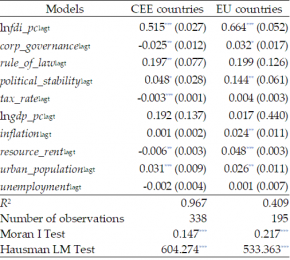
Notes: *** – significance at 1% level, ** – significance at 5% level, * – significance at 10% level. ln – denotes the logarithm of the underlying variable. lagt – denotes lagged underlying variable by one period (year) in time. Values of t statistics in parenthesis. CEE countries: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Georgia, Hungary, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Latvia, Lithuania, Macedonia, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Tajikistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan. EU countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland. Source: Author’s estimates based on World Bank and UNCTAD databases.
Our results for the direct and indirect response to a tax policy in CEE countries illustrate this logic. Decreasing tax_rateincreases FDI to the CEE economy enacting this change (see Table 1), as well as to its neighboring countries (see Table 2). This finding is consistent with jurisdictional competition in taxes. That is, a reduction in domestic tax_rate may entail a decrease in the tax rate of a neighboring economy, resulting in a subsequent increase in FDI. (To explicitly confirm the suggested channel, further tax policy analysis would be needed). Interestingly, our results suggest that jurisdictional competition in taxes is only present among CEE economies, but not among EU countries.
In turn, an increase in corp_governance, a measure of corporate governance quality, increases FDI in neighboring countries both in the EU and in the CEE region (see Table 2). A possible interpretation is that an increase in corp_governance in one country may entail an increase in corp_governance in its neighboring economies, resulting in a subsequent increase in FDI. This result suggests proactive competition via corporate governance policy both among the EU countries and the CEE countries.
However, the direct effect differs between the regions. In the EU, an increase in corp_governance increases FDI to the EU economy in question, in line with common wisdom (see Table 1). At the same time, in the CEE region, an increase in corp_governance is followed by a decrease in FDI to that country.
Table 2. Estimation results of SDEM models – spillover effects
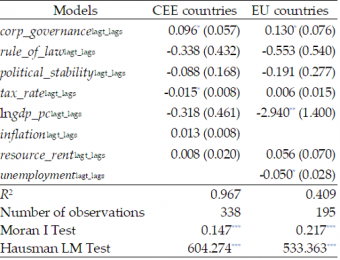
Notes: *** – significance at 1% level, ** – significance at 5% level, * – significance at 10% level. ln – denotes the logarithm of the underlying variable. Values of t statistics in parenthesis. lagt_lags – denotes spatially lagged underlying variable (multiplied by spatial weight matrix) lagged by one period (year) in time. Source: Author’s estimates based on World Bank and UNCTAD databases.
One potential explanation for the negative direct effect of corporate governance quality on FDI in the CEE economies is that improved corporate governance practices can block certain types of FDI, leaving behind foreign investors with a lower “threshold for corruption”. This may decrease FDI to the CEE country in question. However, once the jurisdictional competition results in an improvement of corporate governance across the region, it ultimately has a positive spillover effect.
The above explanation is in line with the theory of regulatory capture (Stigler, 1971), which suggests that the decisions made by public officials might be shaped and sometimes distorted by the efforts of rent-seeking interest groups to increase their influence.
Finally, the estimates do not indicate that the other studied institutional factors, rule of law and political stability, are applied as instruments of jurisdictional competition as neither groups of countries show significant spillover effects. The results, however, show that these factors influence the FDI inflow via the direct effect. More specifically, an increase in political_stability positively influences the FDI inflow to the economies in question, both in CEE and the EU, while rule_of_law is positive and significant only for the CEE countries. If investors are not as responsive to changes in rule_of_law when the initial level is high, the fact that EU countries typically have a higher rule_of_law value compared to CEE countries might explain why this estimate is insignificant for the EU countries.
Conclusion
This brief, first, presents new evidence on the relationship between different economic and institutional factors and FDI using a spatial econometric approach; second, it analyzes the possible existence of jurisdictional competition among developing CEE countries and developed EU countries as well as its effect on FDI.
The results suggest proactive jurisdictional competition in FDI determinants such as corporate governance quality and tax rates. CEE countries competing with one another use both these instruments of jurisdictional competition, while EU countries compete only via corporate governance quality. Furthermore, foreign investors are not sensitive to the quality of rule of law in the EU countries, while this instrument is more important for the FDI inflow to CEE economies.
Our results stress that officials responsible for the FDI policy implementation should pay more attention to the policies undertaken by neighboring governments as such external policies can make their own strategies to attract FDI to their economy less effective.
References
- Blanton, S., and R. Blanton. (2007). What Attracts Foreign Investors? An Examination of Human Rights and Foreign Direct Investment. The Journal of Politics, 69(1), 143-155.
- Blonigen, B. (2005). A Review of the Empirical Literature on FDI Determinants. Atlantic Economic Journal, 33(4), 383-403.
- Elhorst, J. (2014). Spatial Econometrics from Cross-Sectional Data to Spatial Panels. Berlin: Springer.
- Elhorst, J., and S. Freret. (2009). Evidence of Political Yardstick Competition in France Using a Two-Regime Spatial Durbin Model with Fixed Effects December. Journal of Regional Science, 49(5), 931-951.
- IMF (2003). World Economic Outlook 2003. International Monetary Fund: Washington DC.
- LeSage, J. (2014). What Regional Scientists Need to Know About Spatial Econometrics? Working Paper, Texas State University-San Marcos, San Marcos.
- LeSage, J., and R. Pace. (2009). Introduction to Spatial Econometrics. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
- Mazol, A., and S. Mazol. (2021). Competition of Jurisdictions for FDI: Does Developing and Developed Countries Response Different to Economic Challenges? BEROC Working Paper Series, WP no. 73.
- Stigler, G. (1971). The Theory of Economic Regulation. Bell Journal of Economic and Management Science, 2, 3-21.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in policy briefs and other publications are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect those of the FREE Network and its research institutes.
Why Are Women Underrepresented in Politics: Exploring Causes and Solutions

Why are women underrepresented in politics? Despite progress in gender equality, women are still significantly underrepresented in political offices worldwide, especially in higher-level positions. This issue has drawn increasing attention in both academic and policy circles.
Recent research in economics and political science explores the key reasons why women are underrepresented in politics, often categorizing them into “supply-side” and “demand-side” factors. Supply-side factors include women’s potentially lower willingness or ability to run for political office, influenced by social norms, family responsibilities, or lack of political networks. On the demand side, voter and party leader biases against women candidates play a significant role in limiting opportunities for women to hold political office.
Understanding why women are underrepresented in politics is critical for designing effective policies that address the gender gap in political representation. Solutions such as gender quotas, political leadership training for women, and reforms to reduce bias have been proposed. We review some of these strategies and assess their effectiveness based on available evidence.
By tackling the root causes of why women are underrepresented in politics, we can create more inclusive political systems that better reflect the diverse populations they serve.
Country Reports
| Belarus country report (EN) | Belarussian language version (BY) |
| Georgia country report (EN) | Georgian language version (GE) |
| Latvia country report (EN) | Latvian language version (LV) |
| Poland country report (EN) | Polish language version (PL) |
| Russia country report (EN) | Russian language version (RU) |
| Ukraine country report (EN) | Ukrainian language version (UA) |
Women in Politics: Why Are They Under-represented?
Women are generally under-represented in political offices worldwide, and their under-representation becomes larger in more senior positions. Of the four dimensions considered in the World Economic Forum’s Gender Equality Index (namely, Economic Opportunity and Participation, Educational Attainment, Health and Survival and Political Empowerment), the dimension called Political Empowerment, which measures the extent to which women are represented in political office, records the poorest performance, with only 25% of an hypothetical 100% gap having been closed to date.
Importantly, although there is large variation across countries, gender inequality in political empowerment is documented in every region worldwide, including in those countries that are most socially and economically advanced. Sweden, for instance, while having a good record of women’s representation in most institutions (women currently represent 47.5% of the Parliament members, 54.5% of the ministers, and about 43% of the municipal councilors), has never had a woman as Prime minister, and only one-third of its mayors are female. Countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia have only closed 15% of a hypothetical 100% gender gap in political empowerment, according to the World Economic Forum, by far their worst performance among the four sub-indexes that compose the overall Gender Equality Index.
Given the persistent under-representation of women in political institutions, where important decisions that shape societies are taken, economists and political scientists, among others, are increasingly interested in understanding the causes of the gender gap in political representation. In this brief, some of the recent academic literature on this question is summarized, and some policies that may help to close the gender gaps in political representation are reviewed.
Table 1. World Economic Forum Gender Equality Index. Regional Performance in 2020, by Sub-index

Table 1. World Economic Forum Gender Equality Index. Regional Performance in 2020, by Sub-index
Why Are Women Under-represented in Political Office?
Broadly speaking, three main reasons are most often explored, namely women’s unwillingness to become politicians, voters’ bias, and parties’ bias. Below an overview of some of the work that has addressed each of these three factors is provided.
Gender Gaps in Political Ambition
Large-scale surveys have documented that women who, based on their professional and economic credentials, are potential political candidates, report lower ambition to occupy executive offices than comparable men (Fox and Lawless, 2004). The main reasons for the gender gap in ambition appear to be that
- (a) women are less encouraged to run for office than men and
- (b) women are less likely to believe that they are qualified for office than men.
Women’s tendency to shy away from competition (Niederle and Vesterlund, 2007) may also play a role since the political selection process is likely perceived as highly competitive. As Preece and Stoddard (2015) find by using two experiments, priming individuals to consider the competitive nature of politics lowers women’s interest in running for political office, whereas it has no effect on the interest of men.
Women’s willingness to advance in their political careers can also be influenced by family and relational considerations. Recent work from Folke and Rickne (2020) shows that in Sweden female politicians who are promoted to mayor (i.e. the highest office in municipal politics) experience a significant increase in the likelihood of divorcing their partner, whereas this is not the case for men. If women face higher costs for their career achievements, as the evidence in Folke and Rickne (2020) suggests, they may be discouraged from pursuing such objectives.
While there is evidence that women may on average be less willing to advance to top positions than men, it is not clear how quantitatively relevant this factor is to account for the lack of women in power. The introduction of gender quotas in candidate lists in different countries worldwide can be informative in this sense. If women’s under-representation in electoral lists is mostly due to the lack of qualified female politicians, some electoral lists (in most cases representing specific political parties) may not be able to run due to the introduction of a quota, and the average “quality” of lists, measured by some relevant (to voters) characteristics of their members, would decrease. The literature finds no evidence of either of these two responses to quotas (see Baltrunaite et al., 2014, Besley et al., 2017, Bagues and Campa, 2020). On the contrary, in Italy (Baltrunaite et al., 2014) and Sweden (Besley et al., 2017) quotas appear to have improved the “quality” of the elected politicians.
Voters’ Bias
Krook (2018) observes that the existing work in political science regarding the importance of voters’ bias in explaining women’s underrepresentation in politics leads to ambivalent conclusions. Results in the most recent economics literature confirm this assessment. Barbanchon and Sauvagnat (2019) compare votes received by the same female candidate in French parliamentary elections across different polling stations within an electoral district and find that votes for women are lower in municipalities with more traditional gender-role attitudes. They interpret this pattern as evidence of voters’ discrimination and conclude that voters’ bias matters quantitatively in explaining women’s under-representation among politicians. Conversely, Bagues and Campa (2020) find no evidence of voters’ bias against women, based on voters’ reaction to the introduction of a gender quota for electoral lists in Spain. Specifically, they study how the quota impacts the electoral performance of lists that were more affected by the quota – i.e. that were forced to increase their share of female candidates by a larger extent, due to their lower level of feminization pre-quota. They do not find evidence that such lists have worsened their relative electoral performance due to the quota. Put differently, there is no evidence that voters lower their electoral support of a list when its share of female candidates increases for exogenous reasons.
Survey data on voters’ attitudes can also help in gauging the extent to which voters discriminate against women. Based on data from the latest wave of the World Value Survey (WVS, 2017-2020), in Western Europe typically less than 20% of survey respondents express agreement with the statement “Men make better political leaders than women do” (e.g. 5% in Sweden, 9% in Denmark and Germany, 12% in Finland and France, 19% in Italy; only in Greece the share of the agreement is higher than 20%, at 26%). As shown in Figure 1, these percentages are substantially higher in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.).
Figure 1. Share of survey respondents who report to “Agree” or “Strongly Agree” with the statement “Men make better political leaders than women do”.
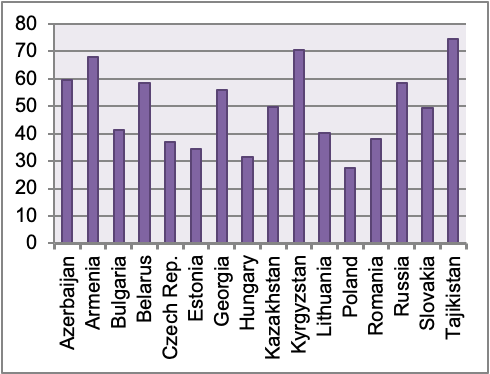
Notes: Data are based on the latest wave of the World Value Survey, 2017-2020. The countries selected were either part of the former Soviet Union or under direct Soviet influence before 1990.
It bears noting, however, that answers to the WVS are not always informative about the extent to which voters’ bias prevails in a country. Where the percentage of respondents who think that men make better political leaders than women is close to or above 50%, as e.g. in Armenia, Georgia, or Russia, voters’ bias is likely to be an important factor. However, in countries with lower levels of agreement, such as for instance Poland, drawing conclusions is harder, since the WVS does not measure the share of respondents who think that women make better political leaders than men do.
Parties’ Bias
Party leaders, who often are key players in the selection of politicians, may prefer to promote male rather than female candidates. If they are aware of voters’ bias against women, preferring male candidates is consistent with a votes-maximizing strategy. However, party leaders may also act as gate-keepers and hold women back even in absence of voters’ bias. Esteve-Volart and Bagues (2012) find evidence of an agency problem between voters and parties by looking at Spanish elections. While parties tend to nominate women in worse positions on the ballot, there is no evidence that women attract fewer votes than men; moreover, when the competition is stiffer, women’s position on the ballot improves. These two facts lead the authors to conclude that the disadvantage women face can likely be attributed to parties’ rather than voters’ bias.
When considering all these factors, it is also important to note that the systematic under-representation of women in political institutions is likely self-reinforcing, due to gendered group dynamics. In the laboratory, women in male-majority teams appear significantly less likely to put their name forward as team-leaders than women in female-majority teams; they anticipate, correctly, lower support from team members (see Born et al., 2019). Female mayors in Italy are significantly more likely to be removed by their municipal councils than their comparable male colleagues; importantly, this is especially true when the share of male councilors is particularly large (Gagliarducci and Paserman, 2011). These studies suggest that, since the political arena has been historically male-dominated, gendered group dynamics can create vicious cycles of women’s under-representation.
Which Policies Can Be Used to Increase Women’s Representation in Political Institutions?
Different policies can be considered to address the various factors accounting for women’s under-representation in politics. In an attempt to address the ”supply-side’’ aspect of women’s under-representation, various non-profit organizations have offered training programs aimed at providing women with knowledge, skills, and networks to build political careers (see, for instance, NDI 2013). While reviewing the existing literature on these programs is beyond the scope of this brief, to the best of the author’s knowledge, there is little to no research-based evidence on the quantitative impact of training on women’s advancements in politics. Non-profit organizations, political parties, and researchers may fruitfully collaborate to implement and systematically test training programs.
Gender quotas are the most commonly used policy intervention, especially those regulating the composition of candidate lists, and they have been extensively studied; overall the literature suggests that quotas are more or less effective in empowering women depending on their design and the context where they are used (see Campa and Hauser, 2020 for a more comprehensive review of the economics literature on gender quotas and related policy implications). Given the nuances in the functioning of quotas, countries or regions that consider their adoption should consult with experts who know the ins and outs of such policies and combine their expertise with local knowledge of the relevant context.
The structure and distribution of power within parties are likely crucial for improving women’s political representation. Some scholars have devoted attention to the role of women’s organizations within parties. Theoretically, such organizations should favour the creation of networks and offer mentorship services, which are likely crucial to climb the career ladder in politics. In Sweden, a coalition of women from both the right and the left is credited for having pressed the Social Democrats’ into adopting their internal zipper quota by threatening to form a feminist party (see Besley et al., 2017). Women’s wings within political parties could play a similar role. Kantola (2018) notes that women’s organizations seem to be currently deemed as outdated, at least in European parties; Childs and Kittilson (2016), on the other hand, find that their presence does not seem to harm women’s promotion to executive roles within parties, a concern that has been associated with the existence of such organizations. In countries with public funding of political parties, specific funds could be directed to women’s organizations within parties.
Folke and Rickne (2020) also note that, since women in top jobs appear to face more relational and family constraints than men, policies that improve the distribution of economic roles within couples could help address the under-representation of women in positions of political power; their observation underlines the crucial role of gender-role attitudes in affecting women’s empowerment in any area of society. How can these attitudes change? An increasing amount of research is being devoted to answering this question. Campa and Serafinelli (2019), for instance, show that a politico-economic regime that puts emphasis on women’s inclusion in the labor market can change some of these attitudes. More research from different contexts and on specific policies will hopefully provide more guidance for policy makers on this important aspect, but the message from the existing research is that gender-role attitudes can be changed, and therefore policy-makers should devote attention to interventions that can influence the formation of such attitudes.
In many Western democracies, the rate of progress in women’s access to top political positions has proven especially slow. This history of Western democracies and the existence of the self-reinforcing mechanisms described above can serve as a lesson for countries in transitions, where new political organizations and institutions are emerging. In absence of specific policies that address women’s under-representation at lower levels very early on, it would likely take a very long time before gender gaps are closed at higher levels of the political hierarchy.
In conclusion, the authors observe that constant monitoring of the gender gaps in political institutions is important, even in presence of clear upward trends, since progress is rarely linear and therefore needs continuous nurturing.
About FROGEE Policy Briefs
FROGEE Policy Briefs is a special series aimed at providing overviews and the popularization of economic research related to gender equality issues. Debates around policies related to gender equality are often highly politicized. We believe that using arguments derived from the most up to date research-based knowledge would help us build a more fruitful discussion of policy proposals and in the end achieve better outcomes.
The aim of the briefs is to improve the understanding of research-based arguments and their implications, by covering the key theories and the most important findings in areas of special interest to the current debate. The briefs start with short general overviews of a given theme, which are followed by a presentation of country-specific contexts, specific policy challenges, implemented reforms and a discussion of other policy options.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in policy briefs and other publications are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect those of the FREE Network and its research institutes.
Media Freedom in Eastern Europe

In recent years, press freedom in many Eastern European countries has increasingly come under threat. This policy brief provides an overview of the importance of a free press for democracy and the challenges to media freedom in these European transition economies.
Introduction
Freedom of expression – which encompasses media freedom – is a fundamental human right enshrined in most countries’ constitutions. Yet for many of their citizens, it is more of an aspiration than a reality. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, a number of countries in Eastern Europe embarked on a process of democratisation and accession to the European Union – for which one of the prerequisites is a free press.
Figure 1 shows a measure of press freedom for the eight Eastern European countries that joined the EU in 2004. These countries saw a general improvement in press freedom from the early 1990s to the early 2000s. But since then, experiences have diverged and in 2017 only Estonia and the Czech Republic showed better scores on press freedom than when they first joined the EU. This pattern of backsliding is not confined to the media, but is also evident in other measures of democracy.
Figure 1. Media Freedom in Eastern Europe
Media and Democracy
A free press and a strong democracy are mutually reinforcing. Research, from mainly Western democracies, shows that the media plays an important role in informing the electorate and holding politicians accountable. For example, Snyder and Strömberg (2010) find that U.S. voters are less informed about their Congressmen when they are covered less in the local press. This is ultimately damaging for voters, as these politicians work less for their constituency and these constituencies also receive less federal funding.
Investigative journalism can play an important role in uncovering corruption and other forms of wrongdoing by politicians. For instance, using the Panama Papers and other leaked documents, journalists uncovered 11,562 offshore entities linked to Russia, 2943 linked to Latvia, and 103 linked to Sweden (see: Offshore Leaks Database). While there are legitimate uses for these offshore entities, the lack of transparency surrounding offshore finance also facilitates tax evasion and money laundering. The revelations of offshore holdings became an embarrassment to many politicians, with some forced to resign. In Russian media, the allegations that the leaks document suspected money laundering by President Putin were characterised as US propaganda (Hoskins and Shchelin, 2018).
Figure 2 shows the relationship between the length of time a country’s leader has been in office and its press freedom score in 2020. While there is no systematic relationship between leader tenure length and press freedom in Western Europe (in blue), across Eastern Europe (in red), countries whose leader has been in power for longer tend to have less media freedom. This correlation is likely to reflect three factors: 1) media coverage can affect a government’s chances of staying in power; 2) a longer-lived government might be more able to control the media and 3) a host of other factors, such as the public’s political engagement and the strength of democratic institutions, could influence both freedom of the press and the longevity of governments.
Figure 2. Media Freedom and Leader Tenure
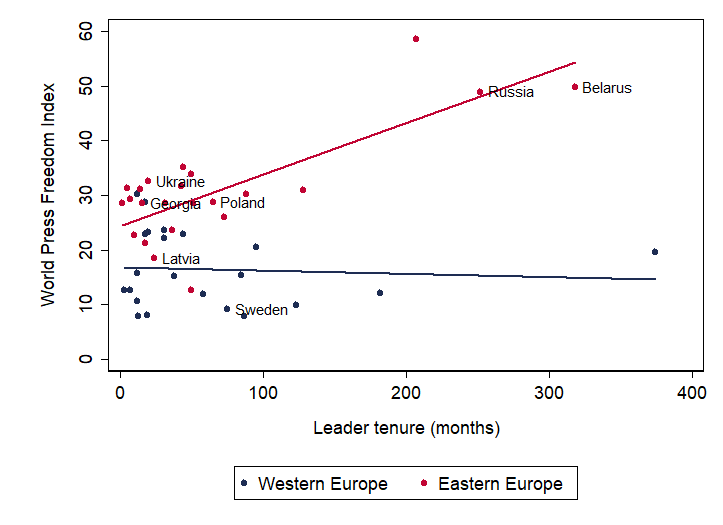
Source: Freedom of the Press, Freedom House. This figure shows the Freedom of the Press total score for the 8 central and eastern European countries that joined the EU in 2004 from 1993 to 2017. A country with a score between 0 and 30 (31 and 60) is designated as having a free (partly free) press.
Electoral Effects of the Media
A number of papers show the causal effects of (biased) media coverage in shaping support for political parties. For instance, watching Fox News increases voting for the Republican party in the US (DellaVigna and Kaplan, 2007; Martin and Yurukoglu, 2017).
Enikolopov, Petrova, and Zhuravskaya (2011) investigate the influence of NTV (the only national TV channel that was at the time independent of the government) on voting in the 1999 parliamentary election in Russia. They find that areas with greater access to NTV were significantly less likely to vote for the government party and more likely to vote for opposition parties.
Biased media can also be used as a foreign policy tool. Peisakhin and Rozenas (2018) find that Ukrainian areas that received Russian TV had on average greater support for pro-Russian parties and candidates in the 2014 elections.
The media landscape in many CEE countries is highly polarised and politicised. Kostadinova (2015) cites research showing that in some former communist countries many journalists still rely on government officials as news sources. In other countries, media in opposition to the communist regimes emerged at the end of the 1980s, such as in Poland where the Gazeta Wyborcza became one of the leading daily newspapers.
Government Control of the Media
Governments have many ways of controlling the media in their country. At the extreme, governments can own and run media outlets, dictate their contents, and censor any dissenting voices. While political and media systems across CEE are diverse, they share some common experiences that might explain their current fragility.
Transitions in Media Ownership
In the Eastern Bloc, the mass media was owned and tightly controlled by the state and used as a tool for propaganda. After the fall of communism, many state-owned media were privatised – along with other state-owned enterprises. Foreign (mostly western European) media conglomerates purchased a significant fraction of media outlets in a number of countries.
While private and foreign ownership of the media can reduce the government’s ability to influence media content, the experience of CEE was not entirely positive. Stetka (2012) argues that while foreign owners brought capital and technology, they were less concerned with transplanting Western journalistic and professional standards. Dobek-Ostrowska (2015) claims that this focus on profit led to the tabloidisation of news across the CEE.
Following the global financial crisis in 2007/2008, foreign investors started to pull out of the CEE media markets and are being replaced by local owners who often have strong links with the government. This is evident in Hungary, where businessmen close to the government have been buying up independent media outlets, including its largest news website, one of two national commercial TV channels, and all regional newspapers (Bede, 2018). The Polish government also aims to “re-nationalise” its media. Plans by a state-run oil company to buy one of the country’s largest media publishers from its German owners were recently approved.
Elsewhere, domestically owned and previously independent media outlets are also being bought by new pro-government owners. In Russia, the formerly independent NTV from the above example was taken over by a state-owned company in 2001 and started to cover the ruling party in the run-up to the following elections in a similarly favourable way to state-controlled TV channels. Gehlbach (2010) argues that Putin’s media strategy is to exert tight control over the news coverage of these three main national television networks, while allowing media outlets with less reach to operate more independently.
In some countries of the region, there is limited information about the ultimate owner of media outlets. Within the EU, Latvia, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Cyprus, are assessed as high risk in terms of transparency of media ownership (Brogi et al. 2020). In 2009, the Swedish company Bonnier sold Diena – one of Latvia’s largest newspapers – to an initially undisclosed investor. A year later, a Latvian businessman acquired a controlling stake in the paper.
Government Advertising
Around the world, traditional news media is facing increased competition from digital platforms and becoming highly dependent on advertising revenue, including advertising from the government and pro-government businesses According to the Centre for Media Pluralism and Media Freedom, there are no clear and fair criteria for the distribution of state advertising to the media in the majority of EU countries – especially those in Eastern Europe (with the exception of Estonia).
Szeidl and Szucs (2021) document how the Hungarian government targeted advertising to friendly media outlets and how these media in turn covered the government more positively. They also present suggestive evidence that a similar favour exchange between government and the media occurs in nine other Eastern European countries, including Poland.
Two weeks ago, many private Polish media outlets coordinated a media blackout to protest government plans to tax advertising revenues. The media companies complained that the tax would cost them $270m a year, while public media received twice as much from taxpayers.
Public Service Media
The establishment of public service media forms an integral part of the EU’s agenda for promoting press freedom. While public service media are an important and trusted source of unbiased information in many western European countries, they generally play a smaller role in the Eastern European media markets. Furthermore, no laws are guaranteeing the independence of public service media from the government in eastern EU countries, with the exception of the Baltic states and Slovenia (see Centre for Media Pluralism and Media Freedom).
Intimidation of Journalists
Governments can also ensure positive coverage by intimidating editors and journalists. Since 1992, 91 journalists were killed, imprisoned, or went missing in Russia, 18 in Ukraine, 15 in Belarus, and 8 in Georgia (data by the Committee to Protect Journalists). While not all of these cases reflect government action, several recent examples illustrate how the judicial system may be used against journalists. For instance, according to the CPJ, ten journalists were imprisoned in November 2020 for covering protests against President Lukashenko in Belarus and one journalist was charged with high treason and espionage in Russia in July 2020.
There are also fears that governments can use defamation laws to deter and punish unwelcome media reports. For instance, the head of Poland’s ruling party filed a libel charge against two journalists from the Gazeta Wyborcza for reporting about his alleged involvement in a real estate project (see, e.g. Council of Europe media freedom alert).
Conclusion
The media plays a vital role in shaping the public debate and holding those in power accountable to the wider population. This power of the media also increases the risk that governments attempt to influence media content.
In recent years, many countries in CEE have seen press freedom come increasingly under threat, undermining some of the progress made since the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Part of the present fragility of media freedom in Eastern Europe may be due to their historical experience. During the transition from communism, many formerly state-owned media companies were sold to private and often foreign owners. In the past decade, local business interests with strong ties to the government started to buy up large shares of the media market in a number of Eastern European countries. Meanwhile, public service media have been less successful at establishing themselves as important and unbiased sources of information across Eastern Europe compared to Western Europe. To ensure positive media coverage, many governments adopt a carrot and stick approach: state advertising revenues and intimidation of individual journalists.
Article 19 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that “everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers”. To ensure these fundamental rights, there need to be transparent and fair rules governing the ownership, management, and financing of media outlets and safeguards for individual journalists.
References
- Bede, Márton, 2018. “As elections loom, stakes are raised for Hungarian media.” International Press Institute.
- Brogi, Elda, Roberta Carlini, Iva Nenadic, Pier Luigi Parcu and Mario Viola de Azevedo Cunha, 2020. ”Monitoring Media Pluralism in the Digital Era.”, Centre for Media Pluralism and Media Freedom Report.
- DellaVigna, Stefano, and Ethan Kaplan. “The Fox News effect: Media bias and voting.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 122, no. 3 (2007): 1187-1234.
- Dobek-Ostrowska, Bogusława, 2015. “25 years after communism: four models of media and politics in Central and Eastern Europe”. In Democracy and media in Central and Eastern Europe 25 years on, 11-46. Publisher: Peter Lang Edition Editors: Bogusłąwa Dobek-Ostrowska & Michał Głowacki
- Enikolopov, Ruben, Maria Petrova and Ekaterina Zhuravskaya, 2011. “Media and political persuasion: Evidence from Russia.” American Economic Review, 101(7), pp. 3253-85.
- Gehlbach, Scott, 2010. “Reflections on Putin and the Media“, Post-Soviet Affairs, 26:1, 77-87.
- Hoskins, Andrew and Pavel Shchelin, 2018. “Information war in the Russian media ecology: the case of the Panama Papers.” Continuum, 32:2, 250-266.
- Kostadinova, Petia, 2015. “Media in the New Democracies of Post-Communist Eastern Europe.” East European Politics and Societies, 29 (2), 453–66.
- Martin, Gregory J., and Ali Yurukoglu, 2017. “Bias in cable news: Persuasion and polarization.” American Economic Review 107, no. 9: 2565-99.
- Peisakhin, Leonid and Arturas Rozenas. 2018. “Electoral Effects of Biased Media: Russian Television in Ukraine.” American Journal of Political Science, 62: 535-550.
- Snyder, James M., and David Strömberg, 2010. “Press Coverage and Political Accountability.” Journal of Political Economy, 118 (2), 355-408.
- Stetka, Vaclav. “From multinationals to business tycoons: Media ownership and journalistic autonomy in Central and Eastern Europe.” The International Journal of Press/Politics, 17: 4, 433-456.
- Szeidl, Adam, and Ferenc Szucs, 2010. “Media capture through favor exchange.” Econometrica, 89 (1): 281-310.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in policy briefs and other publications are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect those of the FREE Network and its research institutes.
SITE Academic Conference 2019 “The Long Shadow of Transition”

The Stockholm Institute of Transition Economics invites you to our annual Academic Conference at the Stockholm School of Economics which brings together researchers in economics and political science who contribute to our understanding of the political economy of Eastern Europe.
For most countries in Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union, the main building blocks of the economic transition from a command economy to a market economy took around 10 years to accomplish. In terms of political institutions and social norms, though, change has been much slower and more uneven. Weak political checks and balances, corruption and authoritarianism threaten not only the welfare of citizens within these countries but also peace and cooperation in Europe more generally.
This year’s edition of our annual Academic Conference will focus on the Political Economics of Long run Development in Eastern Europe. There is by now a growing academic literature analyzing not only the current consequences of authoritarianism and corruption but also the economic history of the eastern region and how that can account for some of the norms and institutions in place today. The purpose of this event is to bring together scholars in this field for a fruitful exchange of ideas and presentations of the current academic standing on the topic.
Keynote speakers
- KEYNOTE 1: RUBEN ENIKOLOPOV, Rector and Professor at the New Economic School.
- KEYNOTE 2: DANIEL TREISMAN, Professor of Political Science at the University of California, Los Angeles.
- KEYNOTE 3: SERGEI GURIEV, Professor of Economics, Sciences Po.
When and where?
Date:
Monday Dec 16, 2019, 9:00 – 17:00.
Tuesday Dec 17, 2019, 10:00 – 14:30
Place: Stockholm School of Economics, KAW Room 1st floor, Bertil Ohlins gata 4.
RSVP: Please note that the number of seats for this event is limited, therefore we kindly ask you to only register if you know that you will be able to attend.
Last day to register: December 13, 12:30 pm.
Read the full program below!
Contact person:
Gun.Malmquist@hhs.se
ACADEMIC CONFERENCE PROGRAM 2019
The Long Shadow of Transition: The State of Democracy in Eastern Europe

In many parts of Eastern Europe, the transition towards stronger political institutions and democratic deepening has been slow and uneven. Weak political checks and balances, corruption and authoritarianism have threatened democracy, economic and social development and adversely impacted peace and stability in Europe at large. This policy brief summarizes the insights from Development Day 2019, a full-day conference organized by SITE at the Stockholm School of Economics on November 12th. The presentations were centred around the current political and business climate in the Eastern European region, throwing light on new developments in the past few years, strides towards and away from democracy, and the challenges as well as possible policy solutions emanating from those.
The State of Democracy in the Region
From a regional perspective, Eastern Europe has seen mixed democratic success over the years with hybrid systems that combine some elements of democracy and autocracy. Based on the V-Dem liberal democracy index, ten transition countries that have joined the EU saw rapid early progress after transition. In comparison, the democratic development in twelve nations of the FSU still outside of the EU has been largely stagnant.
In recent years, however, democracy in some of those EU countries, such as Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Romania have been in decline. Poland, one of the region’s top performers in terms of GDP growth and life expectancy, has experienced a sharp decline in democracy since 2015. Backlashes have often occurred after elections in which corruption and economic mismanagement have led to the downfall of incumbent governments and a general distrust of the political system. Together with low voter turnout, this created fertile ground for more autocratic forces to gain power helped by demand for strong leadership.
An example from Ukraine illustrated the role of media, both traditional and social, for policy-making. In some countries of the region, traditional media is strictly state-controlled with obvious concerns for democracy. This is less the case in Ukraine, where also social media plays an important role in forming political opinions. The concern is that, as elsewhere, opinions that gain traction on social media may not be impartial or well informed, affecting public perception about policy-making. A recent case showing the popular reaction to an attack on the former governor of the Central Bank suggests that those implementing important reforms may not get due credit when biased and partial information dominates the political discourse on social media.
Another case is the South Caucasian region: Armenia, Georgia and Azerbaijan. The political situation there has been characterized as a “government by day, government by night” dichotomy, implying that the real political power largely lies outside the official political institutions. In Georgia, the situation can be described as a competition between autocracy and democracy, with a feudalistic system in which powerful groups replace one another across time. As a result, trust in political institutions is low, as well as citizens’ political participation.
In the case of Azerbaijan, there is an elected presidency, but in reality, power has been passed on hereditarily, becoming a de facto patrimonial system. Lastly, in Armenia, the new government possesses democratic credentials, but the tensions with neighbouring Azerbaijan and Turkey have given increasing power to the military and important economic powers. Overall, democratisation in these countries has been hindered by a trend for powerful politicians to form parties around themselves and to retain power after the end of their mandates. Also, the historical focus on nation-building in these countries has led to a marked exclusion of minorities and a conflict of national identities.
The last country case in this part of the conference focused on the current political situation in Russia and on the likely outcomes after 2024. The social framework in Russia appears constellated by fears – a fear of a world war, of regime tightening and mass repressions, and of lawlessness – all of them on the rise. Similarly, the economy is suffering, in particular from low business activity, somewhat offset by a boost in social payments. Nonetheless, it was argued that it is not economic concerns, but rather political frustration, that has recently led citizens to take to the street. Despite this, survey data shows that trust in Putin is still over 60%, and that most people would vote for him again. However, survey data also points out that the most likely determinant of this trust is the lack of another reference figure, and that citizens are not averse to the idea of political change in itself. Lastly, Putin will most likely retain some political power after 2024, transiting “from father to grandfather of the nation”.
Voices from the civil society in the region also emphasized the importance of a free media and an active civil society to prevent the backsliding of democracy. With examples from Georgia and Ukraine, it was argued that maintaining the independence of the judiciary, as well as the public prosecutor’s office, can go a long way in building credibility both among citizens and the international community. The European Union can leverage the high trust and hopeful attitudes it benefits from in the region to push crucial reforms more strongly. For example, more than 70% of Georgians would vote for joining the EU if a referendum was held on the topic and the European Union is widely regarded as Georgia’s most important foreign supporter.
Weak Institutions and Business Development
The quality of political and legal institutions strongly affects the business environment, in particular with regards to the protection of property rights, rule of law, regulation and corruption. Research from the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) highlights that the governance gap between Eastern Europe and Central Asia and most advanced economies is still large, even though progress in this area has actually been faster than for other emerging economies since the mid-‘90s. This is measured through enterprise surveys as well as individual surveys. In Albania, for instance, a perception of lower corruption was linked to a decrease in the intention to emigrate equivalent to earning 400$ more per month. Another point concerned the complexity of measuring the business environment and the benefits of firm-level surveys asking firms directly about their own actual experience of regular enforcement. For example, in countries such as Poland, Latvia and Romania the actual experience of business regulation measured via the EBRD’s Business Environment Enterprise Performance Survey, is far worse than one would expect from the World Bank’s well known Doing Business rating.
From the perspective of Swedish firms, trade between Sweden and the region has remained rather flat in the past years, as the complexity and risks of these markets especially discourage SMEs. Business Sweden explained that Swedish firms considering an expansion in these markets are concerned with issues of exchange rate stability, and the institutional-driven presence of unfair competition and of excessive bureaucracy. Moreover, inadequate infrastructure and the presence of bribery and corruption make everyday business operations risky and costly. It was generally emphasized that countries have to create a safe investment environment by reducing corruption, establishing a clear and well enacted regulatory environment, having dependable courts and strengthening domestic resource mobilization. Swedish aid can play a part, but there is a need to develop new ways of delivering aid to make it more effective.
An interesting example is Belarus, that has seen more economic and political stability than most neighbours, but at the same time a lack of both economic and political reforms towards market economy and democracy. Gradually the preference towards private ownership, as opposed to public, has increased in recent years and the country has seen a rising share of the private sector, even without specific privatization reforms. Nonetheless, international businesses are still reluctant to invest due to high taxes, a lack of access to finance as well as to a qualified workforce, but most importantly due to the weak legal system. An exception has been China, and Belarus has looked at the One Belt One Road Initiative as a promising bridge to the EU. Scandals connected with the two main Chinese-invested projects have damped the enthusiasm recently, though.
The economic and political risks of extensively relying on badly diversified energy sources, as is the case with natural gas imports from Russia in many transition states were also discussed. It was shown how some countries such as Ukraine, Poland and Lithuania have improved their energy security by either benefitting from reverse-flow technology and the EU’s bargaining power or building their own LNG terminals to diversify supply sources. However, either of these, as well as other energy security improving solutions are likely to come with an economic cost, though, that not all countries in the region can afford.
A Government Perspective
The main focus of this section was the Swedish government’s new inspiring foreign policy initiative, “Drive for Democracy”. Drawing from a definition of democracy by Kerstin Hesselgren, an early Swedish female parliamentarian, democracy enables countries to realize and utilize the forces of the individual and draw them into a life-giving, value-creating society. It was emphasized that the values of democracy are objectives by themselves (e.g. freedom of expression, respect for human rights) but also that democracy has important positive effects in other areas of human welfare. The Swedish government views democracy as the best foundation for a sustainable society, equality of opportunity and absence of gender or racial bias.
The “Drive for Democracy” specifically identifies Eastern Europe as one of the main frontiers between democracy and autocracy, and the Swedish government promotes human rights and stability through various bilateral programmes through the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, Sida, and multilateral initiatives within the EU, such as the Eastern Partnership. It was also emphasized that democracy is a continuous process that can always be improved, as indeed experienced by Sweden. Political rights were granted to women only in 1919 followed by convicts and prisoners in 1933 and to the Roma people only in 1950. Political and democratic rights are thus never once and for all given, and it is crucial that the dividends from democracy are carried forward to the younger generation.
Conclusion
In sum, the day illustrated clearly how democracy engages all segments of society, from the business sector to civil society, and the potential for but also challenges involved for democratic deepening in Eastern Europe. To get more information about the presentations during the day, please visit our website.
Participants at the Conference
- PER OLSSON FRIDH, State Secretary, Ministry for Foreign Affairs.
- ALEXANDER PLEKHANOV, Director for Transition Impact and Global Economics at EBRD.
- TORBJÖRN BECKER, Director, SITE.
- CHLOÉ LE COQ, Associate Professor, SITE and Professor of Economics, University of Paris II Panthéon-Assas.
- THOMAS DE WAAL, Senior Fellow at Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
- NATALIIA SHAPOVAL, Vice President for Policy Research at Kyiv School of Economics.
- ILONA SOLOGUB, Scientific Editor at VoxUkraine and Director for Policy Research at Kyiv School of Economics.
- KETEVAN VASHAKIDZE, President at Europe Foundation, Georgia.
- MARIA BISTER, Senior Policy Specialist, Sida.
- HENRIK NORBERG, Deputy Director, Ministry for Foreign Affairs.
- YLVA BERG, CEO and President, Business Sweden.
- LARS ANELL, Ambassador and formerly Volvo’s Senior Vice President.
- ERIK BERGLÖF, Professor in Practice and Director of the Institute of Global Affairs, London School of Economics and Political Science.
- KATERYNA BORNUKOVA, Academic Director, BEROC, Minsk.
- ANDREI KOLESNIKOV, Senior Fellow, Carnegie Moscow Center.
Liberal Democracy in Transition – The First 30 Years

This year marks 30 years since the first post-communist election in Poland and the fall of the Berlin Wall. Key events that started a dramatic transition process from totalitarian regimes towards liberal democracy in many countries. This brief presents stylized facts from this process together with some thoughts on how to get this process back on a positive track. In general, the transition countries that joined the EU are still far ahead of the other transition countries in terms of democratic development.
The recent decline in democratic indicators in some EU countries should be taken seriously as they involve reducing freedom of expression and removing constraints on the executive, but should also be discussed in light of the significant progress transition countries entering the EU have shown during the first 30 years of transition. The brief shows that changes in a democracy can happen fast and most often happen around elections, so getting voters engaged in the democratic process is crucially important. This requires politicians that engage the electorate and have an interest in preserving democratic institutions. An important question in the region is what the EU can do to promote this, given its overloaded political agenda. Perhaps it is time for a Greta for democracy to wake up the young and shake up the old.
This brief provides an overview of political developments in transition countries since the first post-communist elections in Poland and the fall of the Berlin Wall 30 years ago. It focuses on establishing stylized facts based on quantitative indices of democracy for a large set of transition countries rather than providing in-depth studies of a small number of countries. The aim of the brief is thus to find common patterns across countries that can inform today’s policy discussion on democracy in the region and inspire future studies of the forces driving democracy in individual transition countries.
The first issue to address is what data to use to establish stylized facts of democratic development in the region. By now, there are several interesting indicators that describe various aspects of democratic development, which are produced by different organizations, academic institutions and private data providers. In this brief, three commonly used and well-respected data providers will be compared in the initial section before we zoom in on more specific factors that make up one of these indices.
The big picture
The three indicators that we look at first are: political rights produced by Freedom House; polity 2 produced by the Polity IV project; and the liberal democracy index produced by the V-Dem project. Figures 1-3 show the unweighted average of these indicators for two groups of countries. The EU10 are the transition countries that became EU members in 2004 and 2007 and include Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia. The second group, FSU12, are the 12 countries that came out of the Soviet Union minus the three Baltic countries in the EU10 group, so the FSU12 group consists of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan.
Figure 1. Freedom House

Source: Freedom House and author’s calculations
Note: Scale inverted, 1 is best and 7 worst score
Figure 2. Polity IV project
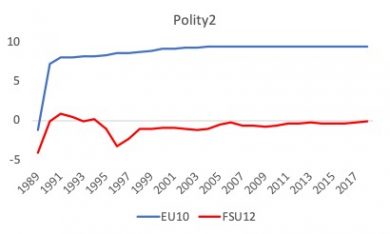
Source: Polity IV project and author’s calculations
Note: Scale from -10 (fully autocratic) to 10 (fully democratic)
Figure 3. V-Dem

Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
Note: Scale from 0 to 1 where higher is more democratic
All three indicators convey the message that the democratic transformation in the EU10 group was very rapid in the early years of transition and the indicators have remained at high levels since the mid-90s only to show some decline in the most recent years for two of the three indicators. The FSU12 set of countries have made much less progress in terms of democratic development and remain far behind the EU10 countries in this regard. Overall, there is little evidence at the aggregate level that the democratic gap between the EU10 and FSU12 groups is closing. While the average EU10 country is more or less a full-fledged democracy, the average FSU12 country is at the lower end of the spectrum for all three democracy measures.
The average indicators in Figures 1-3 obviously hide some interesting developments in individual countries and in the following analysis, we will take a closer look at the liberal democracy index at the country level. We will then investigate what sub-indices contribute to changes in the aggregate index in the countries that have experienced significant declines in their liberal democracy scores.
For the first part of the analysis, it is useful to break down the democratic development in two phases. The first phase is from the onset of transition (1989, 1991 or 1993 depending on the specific country) to the time of the global financial crisis in 2009 and the second phase is from 2009 to 2018 (the last data point).
Figure 4. Liberal democracy, the first phase

Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
Figures 4 and 5 compare how the liberal democracy indicator changes from the first year of the period (measured on the horizontal axis) to the last year of the period (on the vertical axis). The smaller blue dots are the individual countries that make up the EU10 group while the red dots are the FSU12 countries. The 45-degree line indicates when there is no change between start and end years, while observations that lie below (above) the line indicate a deterioration (improvement) of the liberal democracy index in a specific country.
In the first phase of transition (Figure 4), all of the EU10 countries increased their liberal democracy scores and the average increase for the group was almost 0.5, going from 0.26 to 0.74. This was a result of many of the countries in the group making significant improvements without any countries deteriorating. The FSU12 group had a very different development with the average not changing at all since the few countries that improved (Georgia and Ukraine) were counterbalanced by a significant decline in Belarus and a more modest decline in Armenia.
Figure 5. Liberal democracy, the second phase
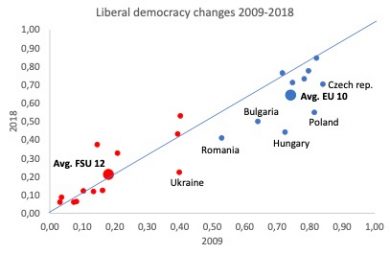
Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
The very rapid improvement in the liberal democracy index in the EU10 countries in the first phase of transition came to a halt and also reversed in several countries in the second phase of transition. Of course, as they had improved so much in the first period, there was less room for further positive developments, but the rapid decline in some of the countries was still negative news. However, it does point towards that reform momentum was very strong in the EU accession process, but once a country had entered the union, the pressure for liberal democratic reforms has faded.
Overall, the EU10 average fell by 0.1 from 2009 to 2018. This was a result of declining scores in several countries. The particularly large declines in this period have been seen in Hungary (-0.28), Poland (-0.27), Bulgaria (-0.14), the Czech Republic (-0.14), and Romania (-0.12). Again, the average FSU12 score did not change much, although Ukraine (-0.2) put its early success in reverse and lost as much in this period as it had gained earlier.
Country developments
Since much of the current discussion centers on how democracy is being under attack, the figures name the countries that have seen significant declines in the liberal democracy score in the first or second phase of transition. Figures 6 and 7 show the time-series of the liberal democracy index in the countries with significant drops at some stage of the transition process.
Figure 6. FSU12 decliners

Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
In many countries, the drop comes suddenly and sharply, with the first and most prominent example being Belarus. There, it only took three years to go from one of the highest ranked FSU12 countries to fall to one of the lowest liberal democracy scores. In Poland, Romania, Bulgaria and Armenia, the process was also very rapid and significant changes happened in 2-3 years.
Figure 7. EU10 decliners
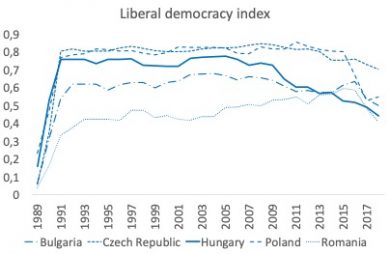
Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
In the Czech Republic and Hungary, the period of decline was much longer and in the case of Hungary, the drop was the most significant in the EU10 group. Ukraine stands out as more of an exception with a roller-coaster development in its liberal democracy score that first took it up the list and then back down to where it started. For those familiar with politics in these countries, it is easy to identify the elections and change in government that have occurred at the times the index has started to fall in all of these countries. In other words, the democratic declines have not started with coups but followed election outcomes where in most cases the incumbent leaders have been replaced by a new person or party.
How democracy came under attack
We will now take a closer look at what has been behind the instances of decline in the aggregate index by investigating how the sub-indices have developed in these countries. The sub-indices that build up the liberal democracy index are: freedom of expression and alternative sources of information; freedom of association; share of population with suffrage; clean elections; elected officials; equality before the law and individual liberty; judicial constraints on the executive; and legislative constraints on the executive (the structure is a bit more complex with mid-level indices, see V-Dem 2019a).
Table 1 shows how these indicators have changed in the time period the liberal democracy indicator has fallen significantly (with shorter versions of the longer names listed above but in the same order). The heat map of decline indicated by the different colours is constructed such that positive changes are marked with green, smaller declines are without colour, declines greater that 0.1 but smaller than 0.2 are in yellow and larger declines in red. Note that the liberal democracy index is not an average of the sub-indices but based on a more sophisticated aggregation technique (see V-Dem 2019b). Therefore, the Czech Republic and Bulgaria can have a greater fall in top-level liberal democracy index that what is indicated by the sub-indices.
Table 1. Changes in liberal democracy indicators at times of democratic decline
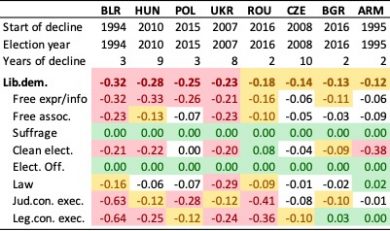
Source: V-Dem project and author’s calculations
For the countries with the largest changes in the liberal democracy index, it is clear that both freedom of expression and alternative sources of information have come under attack together with reduced judicial and legislative constraints on the executive. Among the EU10 countries, Hungary and Poland stand out in terms of reducing freedom of expression, while Romania has seen most of the decline coming from reducing constraints on the executive. Not surprisingly, Belarus stands out in terms of the overall decline in liberal democracy coming from reducing both freedom of expression and constraints on the executive in the most significant way.
On a more general level, the attack on democracy does differ between the countries, but in the cases where serious declines can be seen, the attack has been particularly focused on information aspects and constraints on the executive. At the same time, all countries let all people vote (suffrage always at 1) and let the one with the most votes get the job (elected officials).
Policy conclusions
This brief has provided some stylized facts on the first 30 years of liberal democracy in transition and some details on how democracy has come under attack in individual countries. It leaves open many questions that require further studies and some of these are indeed ongoing in this project and will be presented in future briefs and policy papers here.
Some observations have already been made here that can inform policy discussions on liberal democratic developments in the region. The first is that changes can happen very rapidly, both in terms of improvements but also in terms of dismantling important democratic institutions, including those that provide constraints on the executive or media that provides unbiased coverage before and after elections. What is also noteworthy is that these changes have almost always happened after an election where a new person or party has come to power, so the democratic system is used to introduce less democracy in this sense.
It is also interesting that in all of the countries, the most easily observed indicators of democracy such as suffrage and having the chief executive or legislature being appointed by elections are given the highest possible scores. In other words, even the most autocratic regime wants to look like a democracy; but as the old saying goes, “it is not who votes that is important, it is who counts”.
The regime changes at election times that have led to declining liberal democracy scores have also in many cases come as a result of the incumbents not doing a great job or voters not turning up to vote. It was enough for Lukashenko in Belarus to promise to deal with corruption and rampant inflation that was a result of the old guard’s mismanagement to turn Belarus into an autocracy. In Hungary, the change of regime came after the Socialist leader was caught on tape saying he had been lying to voters. While in Romania, only 39% voted in the 2016 election. And in Bulgaria, around half of the voters stayed at home in the presidential election the same year.
In sum, both incompetent and corrupt past leaders and disengaged or disillusioned voters are part of the decline in a liberal democracy that we have seen in recent years. It is clearly time for policy makers that are interested in preserving liberal democracy in the region and elsewhere to think hard about how democracy can be saved from illiberal democrats. Part of the answer clearly will have to do with how voters can be engaged in the democratic process and take part in elections. It also involves defending free independent media and the thinkers and doers that contribute to the liberal democracy that we cherish. The question is if the young generation will find a Greta for democracy that can kick-start a new transition to liberal democracy in the region and around the world.
For those readers that want to participate more actively in this discussion and have a chance to be in Stockholm on November 12, SITE is organizing a conference on this theme which is open to the public. For more information on the conference, please visit SITE’s website (see here).
References
- Freedom house data downloaded on Oct 4, 2019, from https://freedomhouse.org/content/freedom-world-data-and-resources
- Freedom house methodological note available at https://freedomhouse.org/report/methodology-freedom-world-2018
- Polity IV project data downloaded on Oct 4, 2019, from http://www.systemicpeace.org/inscrdata.html
- Polity IV project manual available at http://www.systemicpeace.org/inscr/p4manualv2018.pdf
- V-Dem project data downloaded on Sept 24, 2019, from https://www.v-dem.net/en/data/data-version-9/
- Coppedge, Michael, John Gerring, Carl Henrik Knutsen, Staffan I. Lindberg, Jan Teorell, David Altman, Michael Bernhard, M. Steven Fish, Adam Glynn, Allen Hicken, Anna Lührmann, Kyle L. Marquardt, Kelly McMann, Pamela Paxton, Daniel Pemstein, Brigitte Seim, Rachel Sigman, Svend-Erik Skaaning, Jeffrey Staton, Steven Wilson, Agnes Cornell, Lisa Gastaldi, Haakon Gjerløw, Nina Ilchenko, Joshua Krusell, Laura Maxwell, Valeriya Mechkova, Juraj Medzihorsky, Josefine Pernes, Johannes von Römer, Natalia Stepanova, Aksel Sundström, Eitan Tzelgov, Yi-ting Wang, Tore Wig, and Daniel Ziblatt. 2019a. “V-Dem [Country-Year/Country-Date] Dataset v9”, Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem)
- Pemstein, Daniel, Kyle L. Marquardt, Eitan Tzelgov, Yi-ting Wang, Juraj Medzihorsky, Joshua Krusell, Farhad Miri, and Johannes von Römer. 2019b. “The V-Dem Measurement Model: Latent Variable Analysis for Cross-National and Cross-Temporal Expert-Coded Data”, V-Dem Working Paper No. 21. 4th edition. University of Gothenburg: Varieties of Democracy Institute.
International Conference on Gender Economics: Removing Obstacles to Gender Equality and Women’s Economic Empowerment

The FREE Network and the International School of Economics at TSU (ISET) and its Policy Institute, are delighted to extend a warm invitation to participate in an international conference on gender economics entitled: “Removing Obstacles to Gender Equality and Women’s Economic Empowerment”.
The conference will be held in Tbilisi, Georgia, on 15-16th November 2019. The conference is organized as part of the FROGEE initiative – the Forum for Research on Gender Economics – supported by the Swedish International Development Agency (Sida) and coordinated by the Stockholm Institute of Transition Economics (SITE).
The objective of the conference is bringing together researchers, policy-makers, and the broader development community to discuss the obstacles to gender equality and women’s economic empowerment, and policies to remove existing constraints, with a focus on Eastern Europe and Emerging Economies.
Our aim is to contribute to the development of national and regional agendas pursuing the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (see UN’s portal here), with a particular focus on Gender Equality (SDG 5), critical to achieving 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
We are currently accepting abstracts (max 500 words) presenting research on, but not limited to, the following topics:
- Gender discrimination in the labour market
- Gender gap in labour force participation
- Gender gap in the allocation of time to unpaid care and domestic work
- Gender gap in leadership positions at all levels of decision-making in political, economic and public life
- Gender gap in the access to ownership and control over land and other forms of property, financial services, inheritance and natural resources.
For all topics, we welcome papers analyzing the causes of the gender gaps and/or potential policy solutions (including the evaluation of the impacts of projects and policies that have already been implemented inside or outside the region).
Important Dates:
Conference dates: 15-16 November 2019. Deadline for abstract submissions: July/10/2019. Notification of acceptance: Jul/31/2019. Full-paper submission deadline, for accepted abstracts: Oct/15/2019.
For more information, please visit the conference website
Revisiting Growth Patterns in Emerging Markets

Recent studies document that emerging markets are rather similar in their growth patterns despite profound differences in starting conditions and productivity fundamentals. This challenges the common view on productivity as the main growth engine. The crucial role of the external environment for emerging markets emphasized by numerous studies adds to this doubt. I argue that productivity fundamentals still matter and remain the core driver of sustainable growth. However, external factors are crucial for understanding deviations from the trajectory of sustainable growth, i.e. episodes of growth accelerations/decelerations.
Challenges for Understanding Growth in Emerging Markets
As we enter the 4th decade of economic transition in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE), the causes and directions of causality of long-term growth in emerging markets might need to be reconsidered. Some recent studies emphasize that growth trajectories in emerging markets are pretty similar, i.e. average growth rates do not differ too much, while jumps and drops in growth rates are synchronous for the bulk of emerging economies (e.g. Fayad and Perelli, 2014). For instance, a decade ago the level of GDP per capita (in 2011 international $) in Macedonia was roughly 45% of that in the Slovak Republic, which likely reflected the productivity (measured through the Global Competitiveness Index) gap between them. During the last decade, Macedonia has roughly closed this productivity gap. Growth theory would postulate that this should have transformed into faster output growth in Macedonia vs. Slovak Republic closing well-being gap. However, the two countries’ had throughout the decade roughly equal average output growth and the well-being gap today is still the same as it was ten years ago.
Such observations seem to conflict with existing theoretical views. First, this is a challenge to the well-being convergence concept that results from growth theory. Moreover, if we measure growth in terms of the speed of closing the well-being gap with respect to the frontier (the US economy), one may argue even for divergence. For instance, Figure 1 presents a scatter-plot for a sample of emerging markets relating the initial conditions – well-being level in 1995 (GDP per capita relative to one of the US economy) – and the average speed of well-being gap (vs. the US economy) closing throughout 1996-2017 (measured in p.p. of corresponding gap ).
Second, the evidence that productivity gains do not automatically trigger output growth challenges a common view that productivity is the major driver for sustainable growth.
Figure 1.Starting Conditions and Well-Being Gains
Source: Own computations based on data from World Development Indicators database (World Bank).
What are possible explanations for the observed similarity in growth rates of emerging markets?
A study by the IMF (2017) suggests a response: growth in emerging markets is similar and synchronous due to the external environment. This study emphasizes the crucial dependence of medium-term growth in developing countries on the following factors: growth of external demand in trade partners, financial conditions, and trade conditions. Moreover, it states that these factors are dominant in explaining the episodes of growth strengthening/weakening.
Does this explanation change the growth nexus for emerging markets? Can one state, that while external factors are crucial for growth and growth in developing countries is rather homogenous, the productivity gains are not so important anymore?
I would say no. First, for better understanding of growth patterns we must clearly compare the relative importance of productivity gains vs. external factors in affecting the growth schedule. Second, we must separate relatively short-term fluctuations in GDP growth from sustainable growth.
Detecting Relative Importance of Growth Drivers
To answer the question about the relative importance of productivity fundamentals and growth factors, I study a panel of 34 emerging market economies (EBRD sample netted from 3 countries for which the data is not available) for 11 years (2007-2017).
To evaluate the relative importance of productivity and external factors, I use a standard approach of running panel growth regressions with fixed effects. At the same time, I make a number of novelties in the research design.
First, for measures of productivity, I engage a unique database – Global Competitiveness Indicators by World Economic Forum (WEF). Although this database provides an insightful perspective on productivity fundamentals at the country level, it is rather seldom a ‘guest’ in economic research. From this database, I extract a number of individual indicators in order to detect which ones among them that have the strongest growth-enhancing effect. For an alternative specification, I use principal components of 9 individual indicators from this database as proxies for productivity gains.
Second, for external factors, I use an approach similar to the IMF (2017) and calculate variables representing external demand growth, trade conditions, and financial conditions (such as a measure of capital inflows) for each country. Moreover, in respect to external demand growth, I use different competing measures (based on either imports of GDP growth of trade partners) and choose the best one in each individual equation. By doing so, I allow this dimension of the external environment to be represented in each model to the largest possible extent.
Third, I depart from using output growth as the only measure of economic growth and response variable in growth regressions. I argue that for international comparison purposes it is worthwhile to consider also the speed of closing the gap towards the frontier (the US economy). On the one hand, this measure is strongly correlated with the traditional output growth rate. On the other hand, this measure, in a sense, nets out the growth rate of a country from global growth, thus capturing something more unique and peculiar just to individual countries’ gains in well-being. Furthermore, I argue that in the discussion about the factors behind growth, one should distinguish between relatively short and long term growth. Annual growth rates, especially at relatively short time horizon, are too dependent on fluctuations, which may be interpreted in terms of growth rate strengthening/weakening. However, to emphasize the property of growth sustainability, we should get rid of ‘unnecessary noise’. For this purpose, I also introduce a trend growth rate measured in a most simple way as the 5 year moving average (following the discussion in Coibion et al. (2017), show that the bulk of measures of ‘potential’ growth are not good enough to get rid of demand shocks and these measures are pretty close to simple moving average measures).
I apply this definition of trend growth both to ‘standard’ GDP growth rate and to the speed of closing the gap towards frontier. So, finally I have 4 response variables: ‘standard’ growth rate, the speed of closing the gap to frontier, and two corresponding measures of trend growth.
Sustainable Growth Mainly Depends on Productivity
Having short-term (annual) growth rate as response variable (either ‘standard’ or the one in terms of closing the gap) provides results close to those in IMF (2017). It may be interpreted in a way that the external environment is more important than productivity factors. If dividing all regressors into two broad groups of factors – external and productivity – the former is responsible for up to 70% of the growth effect, while the latter for about 30%. Among external environment factors, the most important one is financial conditions. Its relative importance is roughly 50% of the group of external factors’ total.
Among productivity fundamentals, an important contributor to short-term growth is the quality of the macroeconomic environment. According to the methodology of WEF (2017), this indicator encompasses the fiscal stance, savings-investment balance, the external position, inflation path, debt issues, etc.
When refocusing from short-term growth to the growth trend as a response variable, the relative importance of the factors behind growth changes. Productivity fundamentals in this case drive up to 80% of growth effect, while external factors are responsible for the remaining 20%. It is worth noting here that the proportion in favor of productivity factors is higher for the concept of closing the gap to frontier rather than for ‘standard’ trend growth rate. This evidence may be interpreted as additional justification for treating this measure of growth as ‘good’ at reflecting individual properties of a country in a global landscape.
Furthermore, the role of individual variables also changes. Among external factors, the most important role in driving sustainable growth belongs to trade conditions and external demand growth, while the role of financial conditions is either miserable or insignificant at most. Among productivity factors as drivers of trend growth, the quality of the macroeconomic environment seems to play a special role, as well as the efficiency of the goods market and the financial system.
Conclusions
The evidence showing rather similar and synchronous growth in emerging markets and recent evidence on the crucial importance of external factors for emerging markets should not lead us to incorrectly believe that productivity fundamentals do not matter anymore. Productivity fundamentals are still the core driver of sustainable growth. At the same time, we should keep in mind the important role of the external environment for emerging markets. However, changes in the external environment are more likely to generate relatively short-term growth rate fluctuations, while having a modest impact on the sustainable growth trajectory. Hence, a country aiming to secure sustainable growth should still first of all think about productivity fundamentals.
References
- Coibion, O., Gorodnichenko, Y, Ulate, M. (2017). The Cyclical Sensitivity in Estimates of Potential Output, National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper No. 23580.
- EBRD (2017). Transition Report 2017-2018, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, London, UK.
- Fayad, G., and Perelli, R. (2014). Growth Surprises and Synchronized Slowdown in Emerging Markets—An Empirical Investigation, IMF Working Paper, WP/14/173.
- IMF (2017). Roads Less Traveled: Growth in Emerging Markets and Developing Economies in a Complicated External Environment, in IMF World Economic Outlook, April, 2017, pp. 65-120.
- World Economic Forum (2017). The Global Competitiveness Report 2017-2018, Geneva: World Economic Forum.
Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in policy briefs and other publications are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect those of the FREE Network and its research institutes.